The Boolean Algebra use a set of Laws and Rules to define the operation of a digital logic circuit
As well as the logic symbols “0” and “1” being used to represent a digital input or output, we can also use them as constants for a permanently “Open” or “Closed” circuit or contact respectively.
A set of rules or Laws of Boolean Algebra expressions have been invented to help reduce the number of logic gates needed to perform a particular logic operation resulting in a list of functions or theorems known commonly as the Laws of Boolean Algebra.
Boolean Algebra is the mathematics we use to analyse digital gates and circuits. We can use these “Laws of Boolean” to both reduce and simplify a complex Boolean expression in an attempt to reduce the number of logic gates required. Boolean Algebra is therefore a system of mathematics based on logic that has its own set of rules or laws which are used to define and reduce Boolean expressions.
The variables used in Boolean Algebra only have one of two possible values, a logic “0” and a logic “1” but an expression can have an infinite number of variables all labelled individually to represent inputs to the expression, For example, variables A, B, C etc, giving us a logical expression of A + B = C, but each variable can ONLY be a 0 or a 1.
Examples: individual laws of Boolean, rules and theorems for Boolean Algebra are given in the following table.
Truth Tables for the Boolean Algebra
|
Boolean |
Description |
Equivalent |
Boolean Algebra |
|
A + 1 = 1 |
A in parallel with |
Annulment |
|
|
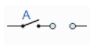
A + 0 = A |
A in parallel with |
Identity |
|
|
A . 1 = A |
A in series with |
Identity |
|
|
A . 0 = 0 |
A in series with |
 |
Annulment |
|
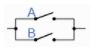
A + A = A |
A in parallel with |
 |
Idempotent |
|
A . A = A |
A in series with |
Idempotent |
|
|
NOT A = A |
NOT NOT A |
|
Double Negation |
|
A + A = 1 |
A in parallel with |
Complement |
|
|
A . A = 0 |
A in series with |
Complement |
|
|
A+B = B+A |
A in parallel with B = |
|
Commutative |
|
A.B = B.A |
A in series with B = |
Commutative |
|
|
A+B = A.B |
invert and replace OR with AND |
|
de Morgan’s Theorem |
|
A.B = A+B |
invert and replace AND with OR |
|
de Morgan’s Theorem |
The basic Laws of Boolean Algebra that relate to the Commutative Law allowing a change in position for addition and multiplication, the Associative Law allowing the removal of brackets for addition and multiplication, as well as the Distributive Law allowing the factoring of an expression, are the same as in ordinary algebra.
Each of the Boolean Laws above are given with just a single or two variables, but the number of variables defined by a single law is not limited to this as there can be an infinite number of variables as inputs too the expression. These Boolean laws detailed above can be used to prove any given Boolean expression as well as for simplifying complicated digital circuits.
A brief description of the various Laws of Boolean are given below with A representing a variable input.
Description of the Laws of Boolean Algebra
- Annulment Law– A term AND´ed with a “0” equals 0 or OR´ed with a “1” will equal 1
-
- A . 0 = 0A variable AND’ed with 0 is always equal to 0
- A + 1 = 1A variable OR’ed with 1 is always equal to 1
- Identity Law– A term OR´ed with a “0” or AND´ed with a “1” will always equal that term
-
- A + 0 = AA variable OR’ed with 0 is always equal to the variable
- A . 1 = AA variable AND’ed with 1 is always equal to the variable
- Idempotent Law– An input that is AND´ed or OR´ed with itself is equal to that input
-
- A + A = AA variable OR’ed with itself is always equal to the variable
- A . A = AA variable AND’ed with itself is always equal to the variable
- Complement Law– A term AND´ed with its complement equals “0” and a term OR´ed with its complement equals “1”
-
- A . A= 0 A variable AND’ed with its complement is always equal to 0
- A + A= 1 A variable OR’ed with its complement is always equal to 1
- Commutative Law– The order of application of two separate terms is not important
-
- A . B = B . AThe order in which two variables are AND’ed makes no difference
- A + B = B + AThe order in which two variables are OR’ed makes no difference
- Double Negation Law– A term that is inverted twice is equal to the original term
-
- A= A A double complement of a variable is always equal to the variable
- de Morgan´s Theorem– There are two “de Morgan´s” rules or theorems,
- (1) Two separate terms NOR´ed together is the same as the two terms inverted (Complement) and AND´ed for example: A+B= A . B
- (2) Two separate terms NAND´ed together is the same as the two terms inverted (Complement) and OR´ed for example: B= A + B
Other algebraic Laws of Boolean not detailed above include:
- Boolean Postulates– While not Boolean Laws in their own right, these are a set of Mathematical Laws which can be used in the simplification of Boolean Expressions.
-
- 0 . 0 = 0A 0 AND’ed with itself is always equal to 0
- 1 . 1 = 1A 1 AND’ed with itself is always equal to 1
- 1 . 0 = 0A 1 AND’ed with a 0 is equal to 0
- 0 + 0 = 0A 0 OR’ed with itself is always equal to 0
- 1 + 1 = 1A 1 OR’ed with itself is always equal to 1
- 1 + 0 = 1A 1 OR’ed with a 0 is equal to 1
- 1= 0 The Inverse (Complement) of a 1 is always equal to 0
- 0= 1 The Inverse (Complement) of a 0 is always equal to 1
- Distributive Law– This law permits the multiplying or factoring out of an expression.
-
- A(B + C) = A.B + A.C(OR Distributive Law)
- A + (B.C) = (A + B).(A + C)(AND Distributive Law)
- Absorptive Law– This law enables a reduction in a complicated expression to a simpler one by absorbing like terms.
-
- A + (A.B) = (A.1) + (A.B) = A(1 + B) = A(OR Absorption Law)
- A(A + B) = (A + 0).(A + B) = A + (0.B) = A(AND Absorption Law)
- Associative Law– This law allows the removal of brackets from an expression and regrouping of the variables.
-
- A + (B + C) = (A + B) + C = A + B + C (OR Associate Law)
- A(B.C) = (A.B)C = A . B . C (AND Associate Law)
Boolean Algebra Functions
Using the information above, simple 2-input AND, OR and NOT Gates can be represented by 16 possible functions as shown in the following table.
|
Function |
Description |
Expression |
|
1. |
NULL |
0 |
|
2. |
IDENTITY |
1 |
|
3. |
Input A |
A |
|
4. |
Input B |
B |
|
5. |
NOT A |
A |
|
6. |
NOT B |
B |
|
7. |
A AND B (AND) |
A . B |
|
8. |
A AND NOT B |
A . B |
|
9. |
NOT A AND B |
A . B |
|
10. |
NOT AND (NAND) |
A . B |
|
11. |
A OR B (OR) |
A + B |
|
12. |
A OR NOT B |
A + B |
|
13. |
NOT A OR B |
A + B |
|
14. |
NOT OR (NOR) |
A + B |
|
15. |
Exclusive-OR |
A . B + A . B |
|
16. |
Exclusive-NOR |
A . B + A . B |
Laws of Boolean Algebra Example: No1
Using the above laws, simplify the following expression: (A + B)(A + C)
|
Q = |
(A + B).(A + C) |
|
|
|
A.A + A.C + A.B + B.C |
– Distributive law |
|
|
A + A.C + A.B + B.C |
– Idempotent AND law (A.A = A) |
|
|
A(1 + C) + A.B + B.C |
– Distributive law |
|
|
A.1 + A.B + B.C |
– Identity OR law (1 + C = 1) |
|
|
A(1 + B) + B.C |
– Distributive law |
|
|
A.1 + B.C |
– Identity OR law (1 + B = 1) |
|
Q = |
A + (B.C) |
– Identity AND law (A.1 = A) |
Then the expression: (A + B)(A + C) can be simplified to A + (B.C) as in the Distributive law.