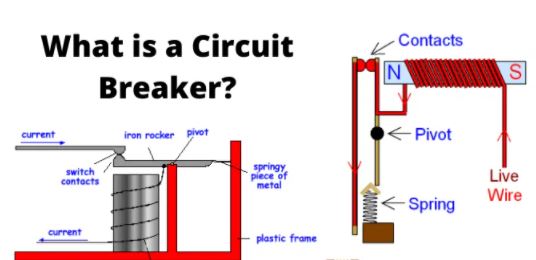
What is Circuit Breaker?
A circuit breaker is a switching device that interrupts the abnormal or fault current. It is a mechanical device that disturbs the flow of high magnitude (fault) current and in additions performs the function of a switch. The circuit breaker is mainly designed for closing or opening of an electrical circuit, thus protects the electrical system from damage.
Introduction to Circuit Breaker
The modern power system deals with huge power network and huge numbers of associated electrical equipment. During a short circuit fault or any other type of electrical fault (such as electric cable faults), a high fault current will flow through this equipment as well as the power network itself. This high current may damage the equipment and networks permanently.
For saving these pieces of equipment and the power networks, the fault current should be cleared from the system as quickly as possible. Again after the fault is removed, the system must come to its normal working condition as soon as possible for supplying reliable quality power to the receiving ends. In addition to that for proper controlling of the power system, different switching operations are required to be performed.
So for timely disconnecting and reconnecting different parts of power system network for protection and control, there must be some special type of switching devices which can be operated safely under huge current carrying condition.
During the interruption of large current, there would be large arcing in between switching contacts, so care should be taken to quench these arcs in circuit breaker in a safe manner. The circuit breaker is the special device which does all the required switching operations during current carrying condition.
Working Principle of Circuit Breaker
The circuit breaker mainly consists of fixed contacts and moving contacts. In normal “ON” condition of the circuit breaker, these two contacts are physically connected to each other due to applied mechanical pressure on the moving contacts. There is an arrangement stored potential energy in the operating mechanism of circuit breaker which is released if the switching signal is given to the breaker.
The potential energy can be stored in the circuit breaker by different ways like by deforming metal spring, by compressed air, or by hydraulic pressure. But whatever the source of potential energy, it must be released during operation. The release of potential energy makes the sliding of the moving contact in a speedy manner.

All circuit breaker have operating coils (tripping coils and close coil), whenever these coils are energized by switching pulse, and the plunger inside them displaced. This operating coil plunger is typically attached to the operating mechanism of circuit breaker, as a result the mechanically stored potential energy in the breaker mechanism is released in forms of kinetic energy, which makes the moving contact to move as these moving contacts mechanically attached through a gear lever arrangement with the operating mechanism.
After a cycle of operation of circuit breaker the total stored energy is released and hence the potential energy again stored in the operating mechanism of the circuit breaker using spring charging motor or air compressor or by any other means.
Till now we have discussed mechanical working principle of circuit breaker. But there are electrical characteristics of a circuit breaker which also should be considered in this discussion of the operation of the circuit breaker. Let’s have a discussion on electrical principle of circuit breaker.
The circuit breaker has to carry large rated or fault power. Due to this large power, there is always dangerously high arcing between moving contacts and fixed contact during operation of the circuit breaker. Again as we discussed earlier the arc in circuit breaker can be quenching safely if the dielectric strength between the current carrying contacts of circuit breaker increases rapidly during every current zero crossing of the alternating current.
The dielectric strength of the media in between contacts can be increased in numbers of ways, like by compressing the ionized arcing media since compressing accelerates the deionization process of the media, by cooling the arcing media since cooling increase the resistance of arcing path or by replacing the ionized arcing media with fresh gasses. Hence some arc quenching processes should be involved in the operation of the circuit breaker.
Although circuit breakers perform their function independently and without supervision, there are also remote control circuit breakers which can be operated on demand at a distance.
Types of Circuit Breaker
Circuit breakers are mainly classified on the basis of rated voltages. Circuit breakers below rated voltage of 1000V are known as the low voltage circuit breakers and above 1000V are called the high voltage circuit breakers.
The most general way of the classification of the circuit breaker is on the basis of the medium of arc extinction. Such types of circuit breakers are as follows :-
- Oil Circuit Breaker
- Minimum Circuit Breaker
- Air Blast Circuit Breaker
- Sulphur Hexafluoride Circuit Breaker
- Vacuum Circuit Breaker
- Air Break Circuit Breaker
All high-voltage circuit breakers may be classified under two main categories i.e oil circuit breakers and oil-less circuit breaker.
According to their services the circuit breaker can be categorized as:
- Outdoor circuit breaker.
- Indoor breaker.
According to the operating mechanism of circuit breaker they can be categorized as:
- Spring operated circuit breaker.
- Pneumatic circuit breaker.
- Hydraulic circuit breaker.
According to the voltage level of installation types of circuit breaker are referred as-
- High voltage circuit breaker.
- Medium voltage circuit breaker.
- Low voltage circuit breaker.