Mostly, the galvanised iron is used for the earthing. The earthing provides the simple path to the leakage current. The shortcircuit current of the equipment passes to the earth which has zero potential. Thus, protects the system and equipment from damage.
What is a Earthing?

The process of transferring the immediate discharge of the electrical energy directly to the earth by the help of the low resistance wire is known as the electrical earthing. The electrical earthing is done by connecting the non-current carrying part of the equipment or neutral of supply system to the ground.
Types of Electrical Earthing
The electrical equipment mainly consists of two non-current carrying parts. These parts are neutral of the system or frame of the electrical equipment. From the earthing of these two non-current carrying parts of the electrical system earthing can be classified into two types.
- Neutral Earthing
- Equipment Earthing.
1. Neutral Earthing
In neutral earthing, the neutral of the system is directly connected to earth by the help of the GI wire. The neutral earthing is also called the system earthing. Such type of earthing is mostly provided to the system which has star winding. For example, the neutral earthing is provided in the generator, transformer, motor etc.
2.Equipment Earthing
Such type of earthing is provided to the electrical equipment. The non-current carrying part of the equipment like their metallic frame is connected to the earth by the help of the conducting wire. If any fault occurs in the apparatus, the short-circuit current to pass the earth by the help of wire. Thus, protect the system from damage.
Importance of Earthing
The earthing is essential because of the following reasons
- The earthing protects the personnel from the shortcircuit current.
- The earthing provides the easiest path to the flow of shortcircuit current even after the failure of the insulation.
- The earthing protects the apparatus and personnel from the high voltage surges and lightning discharge.
Earthing can be done by electrically connecting the respective parts in the installation to some system of electrical conductors or electrodes placed near the soil or below the ground level. The earthing mat or electrode under the ground level have flat iron riser through which all the non-current-carrying metallic parts of the equipment are connected.
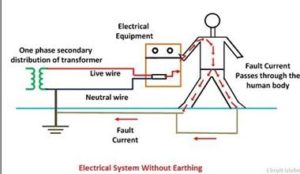
When the fault occurs the fault current from the equipment flows through the earthing system to the earth and thereby protect the equipment from the fault current. At the time of the fault, the earth mat conductors rise to the voltage which is equal to the resistance of the earth mat multiplied by a ground fault.
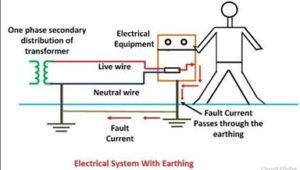
The contacting assembly is called earthing. The metallic conductors connecting the parts of the installation with the earthing are called electrical connection. The earthing and the earthing connection together called the earthing system