An electrical load is a device or an electrical component that consumes electrical energy and convert it into another form of energy. Electric lamps, air conditioners, motors, resistors etc. are some of the examples of electrical loads. They can be classified according to various different factors.
- To indicates a device or a collection of the equipment which use electrical energy.
- For showing the power requires from a given supply circuit.
- The electrical load indicates the current or power passing through the line or machine.
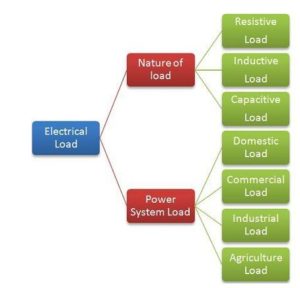
The classifications of loads are shown in the figure below.
Resistive, Capacitive & Inductive Load
Electrical loads can be classified according to their nature as Resistive, Capacitive, Inductive and combinations of these.
1.Resistive Load

- Two common examples of resistive loads are incandescent lamps and electric heaters.
- Resistive loads consume electrical power in such a manner that the current wave remains in phase with the voltage wave. That means, power factor for a resistive load is unity.
2.Capacitive Load
- A capacitive load causes the current wave to lead the voltage wave. Thus, power factor of a capacitive load is leading.
- Examples of capacitive loads are: capacitor banks, buried cables, capacitors used in various circuits such as motor starters etc.
3.Inductive Load
- An inductive load causes the current wave to lag the voltage wave. Thus, power factor of an inductive load is lagging.
- Examples of inductive load include transformers, motors, coils etc.
4.Combination Loads
- Most of the loads are not purely resistive or purely capacitive or purely inductive. Many practical loads make use of various combinations of resistors, capacitors and inductors. Power factor of such loads is less than unity and either lagging or leading.
- Examples: Single phase motors often use capacitors to aid the motor during starting and running, tuning circuits or filter circuits etc.
Types Of Loads In Power System
There are different types of the loads in a power system are as follows.
- Domestic / Residential load
- Commercial load
- Industrial load
- Agriculture load
- Street Light/Traction Load
1. Domestic / Residential Load
Domestic load consists of lights, fans, home electric appliances (including TV, AC, refrigerators, heaters etc.), small motors for pumping water etc. Most of the domestic loads are connected for only some hours during a day. For example, lighting load is connected for few hours during night time.
2. Commercial Load
Commercial load consists of electrical loads that are meant to be used commercially, such as in restaurants, shops, malls etc. This type of load occurs for more hours during the day as compared to the domestic load.
3. Industrial Load
Industrial load consists of load demand by various industries. It includes all electrical loads used in industries along with the employed machinery. Industrial loads may be connected during the whole day.
4. Street Light Load
This type of load consists of street lighting, water supply and drainage systems etc. Street lighting is practically constant during the night hours. Water may be pumped to overhead storage tanks during the off-peak hours to improve the load factor of the system.
5. Agriculture/Irrigation Load
Motors and pumps used in irrigation systems to supply the water for farming come under this category. Generally, irrigation loads are supplied during off-peak or night hours.
6. Electric Traction Load
Electric railways, tram cars etc. come under traction loads. This type of loads reaches its peak during morning and evening hours.
Some Other Classifications Of Electrical Loads
According To Load Nature
- Linear loads
- Non-linear loads
According To Phases
- Single phase loads
- Three phase loads
According To Importance
- Vital electrical loads (e.g. required for life safety)
- Essential electrical loads
- Non-essential / normal electrical loads
Electrical loads may also be classified in may different manners, such as according to their functions.